?? ??????? ???????? ??? ???? ??????? ?????? ??????? ??? ???? ????? "?????? ???????" ???? ????? ????? ???? ????? ?????? ????????. ??? ????????? ???? ???? ??????? ?????????? ??? ??? ??? ????? ????? ????? ?????? ???????. ??? ???????? ?? ????? ?????? ???? ??? ?????? ??? ????? ??? ??????? ?? ?????? ?? ??? ????? ???? ?????? ??? "???????? ????????" ?"?????? ??????"? ???? ??? ????? ???????? ???? ??? ????? ???? ????????? ????????? ??? ???? ?????? ???? ????????? ??????? ??? ???? ??????.
???? ?????? "???????? ????????" ?"?????? ??????" ?????? ???? ????? ??? ?????? ?????? ???? ?????? ???? ?? ???????? ?????????? ??????? ????????? ????? ??? ????????? ??????? ????? ???? ?????? ????????. ???? ??? ???????? ???? ???? ?????? ?????? ??????? ??? ??????? ?????? ???????? ?? ????? ??? ???? ???? ?????? ???? ???? ?? ??? ?????. ?????? ????? ???? ?? ???? ???? ?? ?????? ???? ?????? ???? ????????? ??? ??? ???? ?????? ?? ??? ?????? ???????? ????? ??? ?? ?????? ??????? ???? ???? ??????.
?????? "???????? ????????" ?"?????? ??????" ???????? ?? ??? ????? ??????. ??????? ?????? ???? ????? ?????? ?? ???? ??????? ??? ??????? ?????? ???????? ????????? ???????? ??? ?? ??? ???? ??????? ??????? ??? ????? ??????? ??????? ????????? ????????? ???????? ????? ??? ????? ???????? ?? ????? ?????? ??????? ?????? ???????? ?????????. ??? ???????? ???????? ???? ???? ????? ?? ???? ????? ?????? ??? ???? ???? ????? ??? ??????? ????????? ???? ?????? ????????? ??? ???? ?? ????? ????? ???? ?????? ???????.
?? ??? ????? "???????? ????????" ???? ??? ?? ??? ???? ????? ????? ?????? ?? ????? ?????? "??? ?????" (1983). ???? ?????? ????? ?? ??????? ???????? ??????? ?????? ?? ?????? ?? ????? ??? ??? ???????? ??????? ?? ????????? ?? ???? ?????? ?? ??????? ???????? ???? ???? ?????? ??????. ??? ?? ??????? ???? ????? ?? ????????? ?? ???? ?????? ????? ?????? ???? ????? ?????? ???????:
?????? ??????: ?????? ??? ??????? ??????? ??????? ?????? ????????? ?? ?????? ??? ??????? ?????? ??????.
?????? ??????? ???????: ???????? ????????? ??????? ????????? ?? ????? ??????? ?? ??????? ????????.
?????? ?????? ???????: ?????? ??? ????? ?????? ??????? ?????? ???? ????? ??? ?? ??? ???????? ???????? ???????? ?????????.
?????? ?????? ??????: ??????? ????? ??????? ?? ??????? ????????? ?????? ?????? ?? ?????? ???????? ????????.
?????? ????????: ?????? ??? ??? ?????? ?????? ??????? ?????????? ???????? ??? ???????? ??????? ???????? ????????.
?????? ?????????: ?????? ??? ??????? ?? ??????? ???????? ???? ??????? ???????? ???????? ????.
?????? ??????: ????? ??? ???? ????? ???? ??? ??????? ???????? ???????.
?????? ???????: ?????? ??? ?????? ??? ??????? ????????? ????????? ??????? ???????? ????????.
??? ????? "?????? ??????"? ????? ???? ?? ??? ??? ????? ????? ????? ????????? ?????????. ???? ??? (1987) "????? ??????" ???? "??????? ???????? ?? ??????? ???? ?????? ??????? ??? ?????? ????? ??????". ????? ???? ???? ??? ??????? ?? ???????????? ?????? ???? ???????? ????? ?? ?????? ????????? ????????. ???? ???? ??? ??????? ??? ??????? ??????? ??? ???? ???? ???? (1927) ?????? ?????? ?? ????? ????? ??????? ??????? ??? ??????? ????? ?????? ???????? ??????? ????? ??????? ?????????? ????????? ????? ????????.
??? ??? ??? ???? ????? ?????? ??????? ??????? ??? ?????? ????? "VAK" ???? ???? ??? ??????? (1970). ??? ??????? ???? ????????? ??? ???? ???? ??????: ????????? ????????? ????????? ????????? ?????????? ???????? ?? ????????. ???? ??? ???????? ????? ???? ???? ?????? ????????? ?? ??????? ??? ?? ????? ?? ?????? ?????? ?????? ?? ??? ????? ???? ??? ???? ????? ?? ???? ???? ?????? ????? ????? ?? ???? ??????? ???? ????? ??? ????? ?? ????? ??????? ????? ????? ????? ??????? ??? ???.
In recent years, under the influence of communicative approach, great importance has been placed on the notion of learner centeredness that makes learners at the heart of the educational process. The shift in the learning paradigm of the teaching learning process from teacher-directed to learner-centered has allowed theories of �Multiple Intelligences� and �learner styles� to take over the traditional view that treats learners holistically, as one entity. �Multiple Intelligences� and �learner styles� mark a shift towards more up-to-dated pedagogical notions that cater for individual learners and attest to learners� variation inside the classroom.
The two theories attempt to account for differences traced among individuals and, at lower level, raise the teacher awareness of learners� variations that feature classes. If some people are better at something, respond differently to the same stimulus, then these would suggest that students have different preferred ways of processing knowledge or rather their individual brains operate differently. Multiple Intelligences and Learners� style seem to complete each other. The latter tends to focus on the process of learning and learners personalities: how individuals absorb, think about, and store information while the previous focused on content, and overhauled our definition of intelligence. The premises underlying the two theories carries implications for language teaching which, in turn, would impact the activities teachers carries out in classrooms.
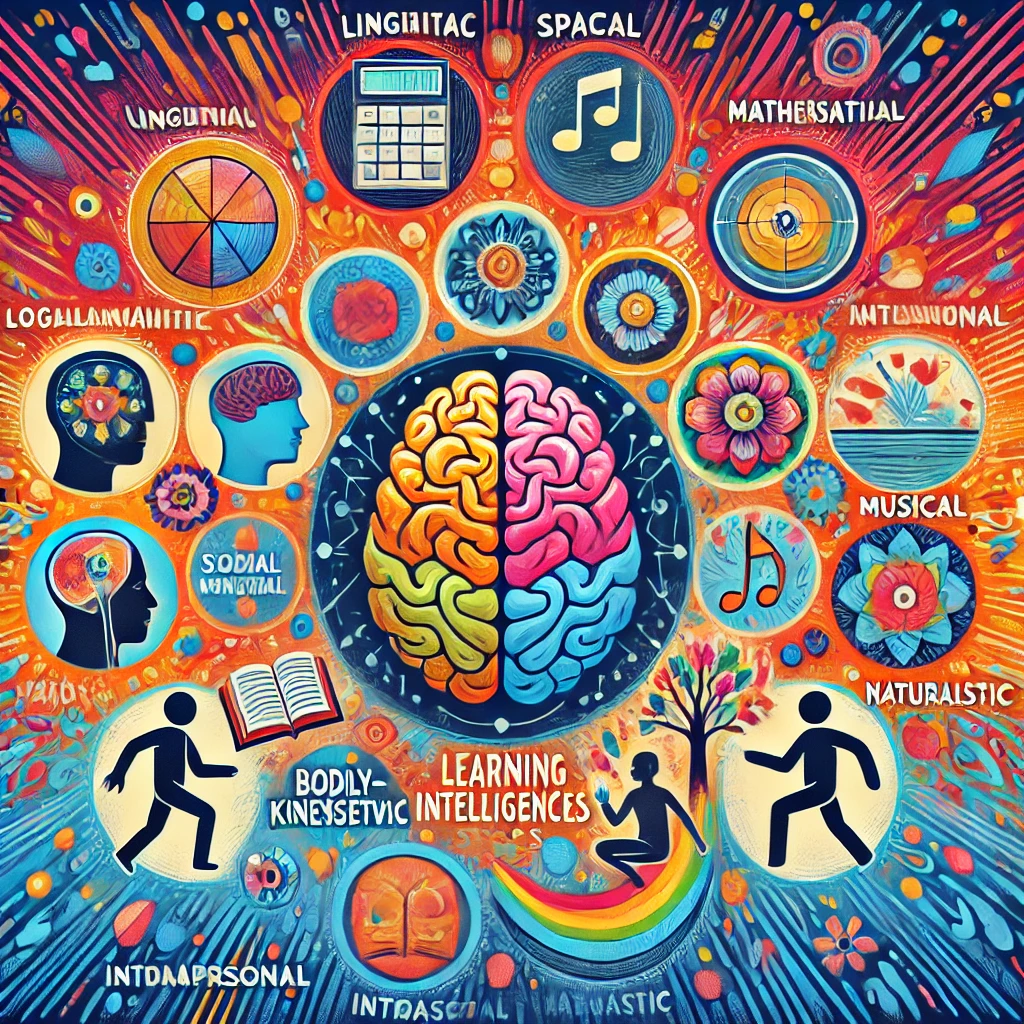
�Multiple intelligences� was identified by the psychologist Howard Gardner in his book �Frames of Mind� (1983). In his book, Gardner re-considers our traditional perception of what intelligence might be. He argued that our definition of intelligence has been determined by our culture, narrowed to mathematical and linguistics. According to Gardner, humans do not possess a single or general intelligence, but a range of intelligences. He initially listed seven �kinds of minds�, then he added the eight one, which he calls naturalist:
1. Linguistic Intelligence: it has to do with an effective use of words orally or in writing, syntactic manipulation of language.
2. Logical-mathematical Intelligence: it involves sensitivity to the use of mathematical and logical patterns and the use of numbers. It is attached to the ability of reasoning.
3. Spatial Intelligence: the ability to perceive the visual-spatial world accurately. This includes recognition of colors, shapes, form, space, and lines.
4. Kinesthetic Intelligence: the use of body to express ideas and feelings. This intelligence would incorporate abilities such as movement, flexibility, and balance.
5. Musical Intelligence: the ability to perceive, discriminate, and transform musical forms. It means also being sensitive to rhythm, pitch, melodies.
6. Interpersonal Intelligence: the ability to socialize easily with people around and to discriminate different moods, intentions, motivations, and feelings. It implies implies being responsive to facial expressions, voice, and body language.
7. Intrapersonal Intelligence: good development of self-knowledge and good awareness of one�s motivation, intentions, mood, and self-esteem.
8. Naturalist Intelligence: it concerns much people who are interested in their surroundings. People who are good at recognition and classification of species, and those who are interested and knowledgeable about natural phenomena.
With regard to learning style theory, it procalims that each person has a preferred way of receiving information. More (1987) stated, �Learning style can be defined as the usual or characteristic manner in which a learner goes about the task of learning�. In other word, it refers to the preferred mood through which a learner acquires and processed information. Learning-style theory has its roots in the psychoanalytic community. It begins with Carl Jung (1927) who noted major differences in the way people perceived: sensation versus intuition, logical thinking versus imaginative feelings, and extroversion versus introversion. Given its importance, various learning styles models exists, each focuses on one some aspects of learners personality, yet one of the most salient and highly acclaimed theoretical model of is the VAK model (Neil Fleming. 1970) . it distinguished three main styles: visual learners; auditory learners; kinesthetic learners or tactile learners. it sometimes which expanded upon earlier Neuro-linguistic programming . Both learners� styles models and Multiple intelligences assert that although a person may be using different styles and intelligences all at once, one is much dominant and articulated in everyone. Everyone has his own �preferred primary system� ( Revell and Norman 1997:32).
#??????? #??????_??????? #??????_???????? #????????_???????? #??????_?????? #??????_??????? #?????_?????? #??????_?????? #??????_???????_??????? #??????_??????_??????? #??????_??????_?????? #??????_???????? #??????_????????? #??????_?????? #??????_??????? #?????_VAK #???_??????? #??????_?????? #??????_?????? #??????_?????? #??????_???????? #????? #????
#Education #Learner_Centered #Communicative_Approach #Multiple_Intelligences #Learning_Styles #Individual_Differences #Howard_Gardner #Linguistic_Intelligence #Logical_Mathematical_Intelligence #Spatial_Intelligence #Bodily_Kinesthetic_Intelligence #Musical_Intelligence #Interpersonal_Intelligence #Intrapersonal_Intelligence #Naturalistic_Intelligence #VAK_Model #Neil_Fleming #Visual_Learning #Auditory_Learning #Kinesthetic_Learning #Classrooms #ifad #rashad

التعليقات
لا توجد تعليقات حتى الآن.
يجب أن تسجل الدخول لإضافة تعليق.